algorithms
sieve of Eratosthenes
classic
def sieve(limit):
import math
check = [True] * max(3, limit + 1)
check[0] = False
check[1] = False
check[2] = True
for i in range(4, len(check), 2):
check[i] = False
sqrt_limit = int(math.sqrt(limit))
for i in range(3, sqrt_limit + 1, 2):
if not check[i]:
continue
for j in range(i * i, len(check), i):
check[j] = False
return [i for i in range(limit + 1) if check[i]]segmented
def segmented_sieve(limit):
import math
sieve_size = 10000
sqrt_limit = int(math.sqrt(limit))
primes = [2]
is_prime = [True] * (sqrt_limit + 1)
for x in range(3, sqrt_limit + 1, 2):
if not is_prime[x]:
continue
primes.append(x)
for m in range(x * x, sqrt_limit + 1, x):
is_prime[m] = False
del is_prime
for start in range(0, limit + 1, sieve_size):
cur_size = min(sieve_size, limit + 1 - start)
block = [True] * cur_size
for p in primes:
i = p * (start // p + bool(start % p)) - start
while i < cur_size:
block[i] = False
i += p
if start == 0:
block[0] = False
block[1] = False
for i in range(0, cur_size):
if block[i]:
primes.append(start + i)
return primesreferences
trial division
def trial_div(limit):
import math
all_primes = [2]
for i in range(3, limit + 1, 2):
is_prime = True
root = int(math.sqrt(i))
for p in all_primes:
if p > root:
break
if i % p == 0:
is_prime = False
break
if is_prime:
all_primes.append(i)
return all_primesDijkstra
def dijkstra(limit):
multiples = [4]
all_primes = [2]
lim_prime_idx = 0 # index of the smallest prime doesn't need to check
for x in range(3, limit + 1, 2): # skip 2
if x >= multiples[lim_prime_idx]:
lim_prime_idx += 1
# next prime already found due to p_{n + 1} < p_{n}^2
multiples.append(all_primes[lim_prime_idx]**2)
is_prime = True
for i in range(1, lim_prime_idx): # skip 2
if multiples[i] < x:
multiples[i] += 2 * all_primes[i] # only odd multiples
if x == multiples[i]:
is_prime = False
break
if is_prime:
all_primes.append(x)
return all_primesintuition
- fox
xin range(primes[i - 1]**2, primes[i]**2)withprimes[i - 1]andprimes[i]are consecutive primes- only need to check for prime factors
< primes[i] - open conjecture: there is a prime number in between the squares of 2 consecutive primes
- related to Legendre’s conjecture
- only need to check for prime factors
- to check for composites, maintain a list of
multiplesof all primes up toprimes[i]multiples[i]is the smallest multiple of theprimes[i]that>= x- only need to extend
multipleswhen the range(primes[i - 1]**2, primes[i]**2)changes multiples[i]is initialized withprimes[i]**2because smaller multiples ofprimes[i]is divisible by some prime< primes[i]
visualization
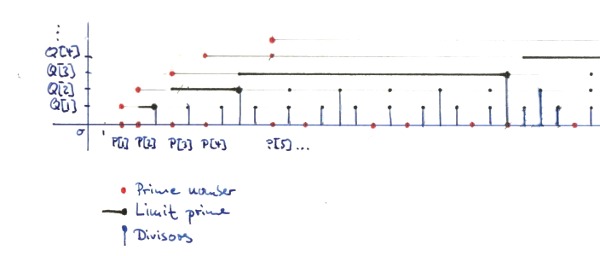 (
(Q is the list of multiples, index starts from 1)
references
- Dijkstra’s Hidden Prime Finding Algorithm - YouTube
- also check the comments
- also check the comments
- Dijkstra’s Prime Number Algorithm
- cs.utexas.edu/users/EWD/ewd02xx/EWD249.PDF
- relies on the mathematical fact that there is a prime between every number and its square - which is surprisingly difficult to prove (see Bertrand’s theorem).
performance comparison
import time
import tracemalloc
limit = 10**6
def profile(func, limit):
t = time.perf_counter()
primes = func(limit)
print("num primes:", len(primes))
print("time:", time.perf_counter() - t)
tracemalloc.clear_traces()
tracemalloc.start()
func(limit)
cur, peak = tracemalloc.get_traced_memory()
tracemalloc.stop()
print("memory:", peak - cur)
print()
print('sieve', '-' * 10)
profile(sieve, limit)
print('segmented sieve', '-' * 10)
profile(segmented_sieve, limit)
print('trial div', '-' * 10)
profile(trial_div, limit)
print('dijkstra' , '-' * 10)
profile(dijkstra, limit)sieve ----------
num primes: 78498
time: 0.3589751999825239
memory: 11143176
segmented sieve ----------
num primes: 78498
time: 1.2164868999971077
memory: 3280104
trial div ----------
num primes: 78498
time: 1.4015573000069708
memory: 3143152
dijkstra ----------
num primes: 78498
time: 0.9058849000139162
memory: 3149888